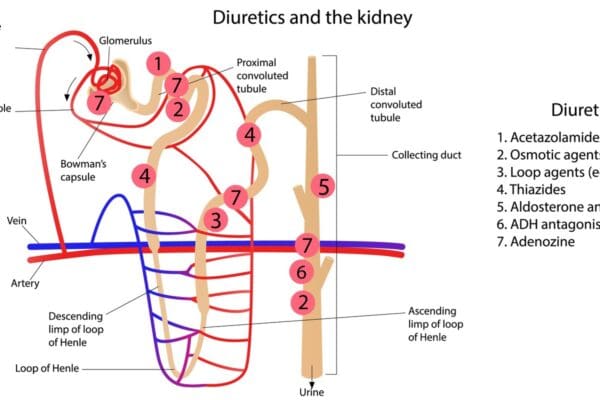
Pharmacology of Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors
Mechanism of Action: Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors (CAIs) act primarily on the proximal convoluted tubule in the kidneys. They inhibit the enzyme carbonic anhydrase, which is essential for the reabsorption of bicarbonate ions. This leads to increased excretion of bicarbonate, sodium, and water, resulting in mild diuresis and acidification of the urine. Pharmacokinetics: Drug Examples: Clinical…