Understanding Beta-Agonists: A Complete Overview for Patients and Healthcare Providers
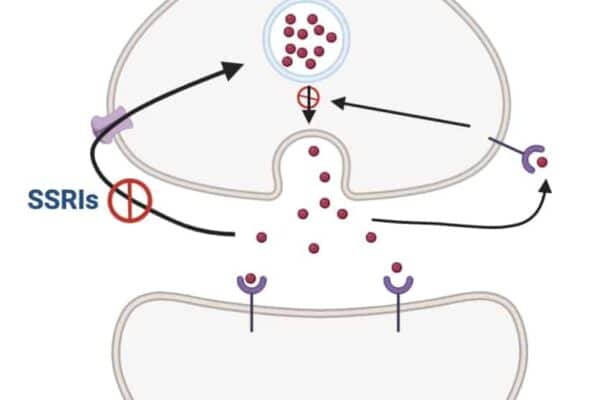
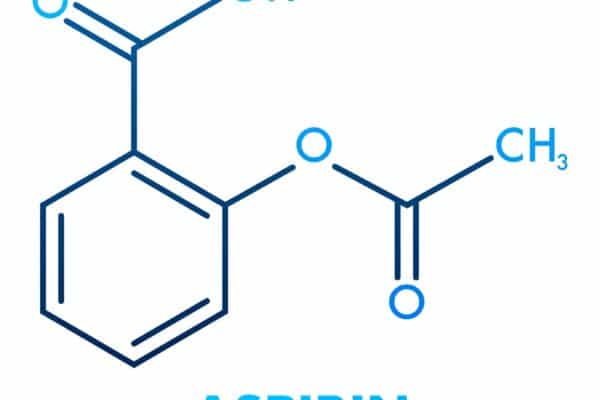
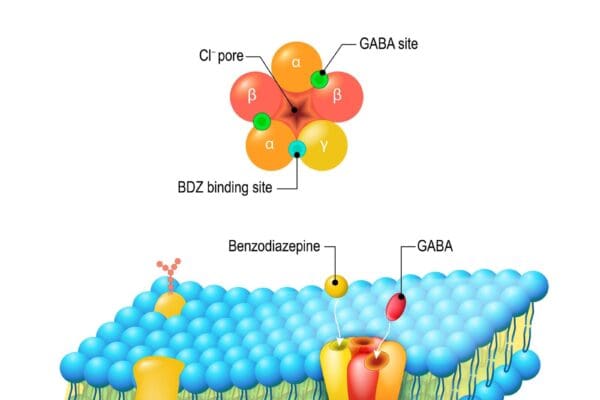
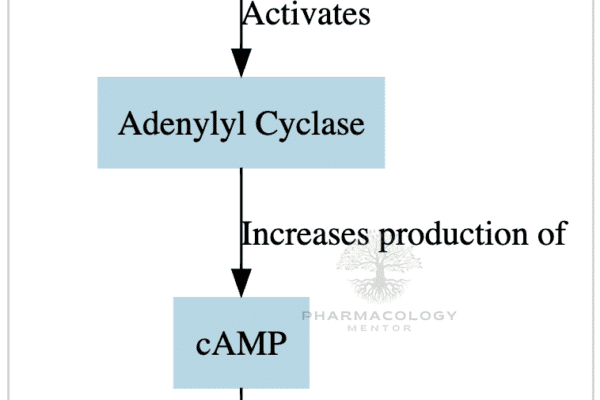
Introduction to Beta-Agonists: Beta-agonists are medications that stimulate beta receptors in the body. These receptors are found in various tissues, including the lungs, heart, and blood vessels. Due to their effects, beta-agonists are commonly used to treat conditions like asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and certain heart conditions. Classification of Beta-Agonists: Mechanism of action:…