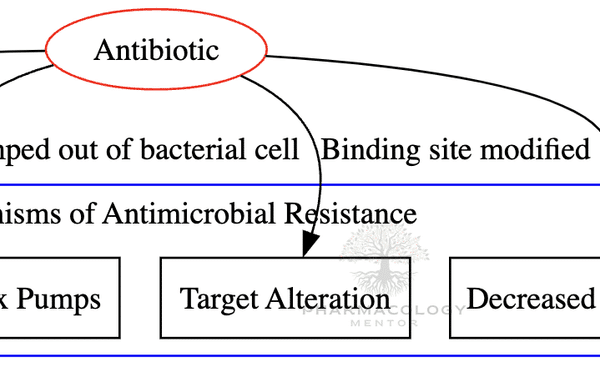
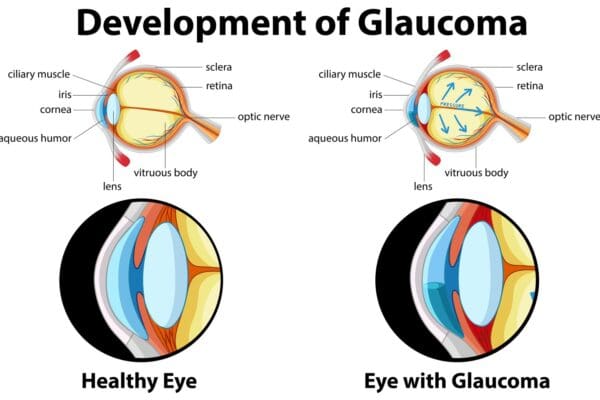
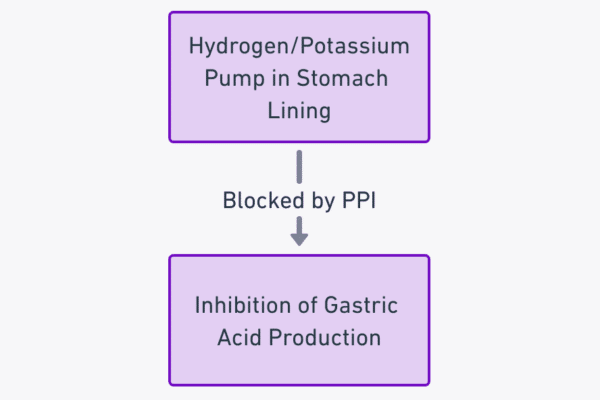
Pharmacology of Antitussives
Introduction of Antitussives Antitussives are drugs that suppress or relieve coughing. They act centrally on the cough center in the medulla oblongata of the brain or peripherally on the cough receptors in the respiratory tract. Classification of Antitussives: a. Opioid Antitussives: Codeine: A mild opioid analgesic also used as a cough suppressant. Hydrocodone: A stronger…