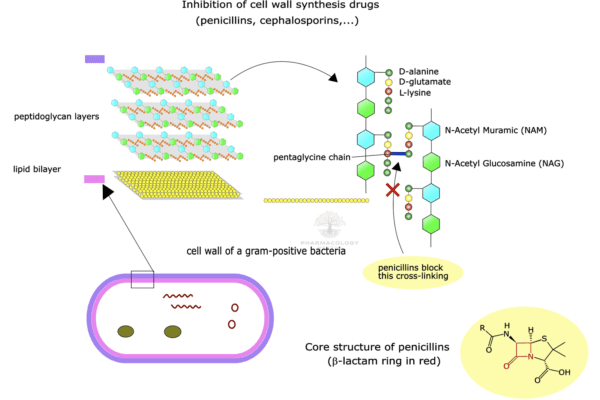
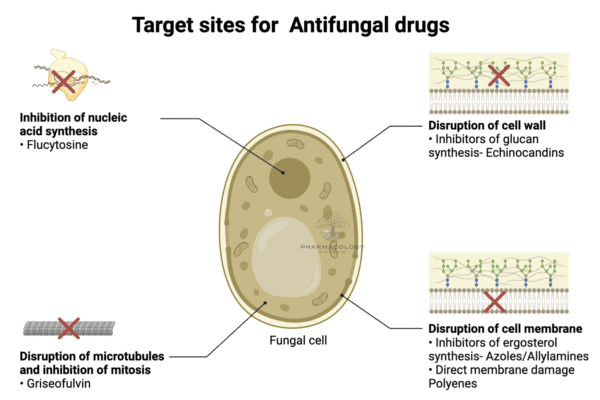
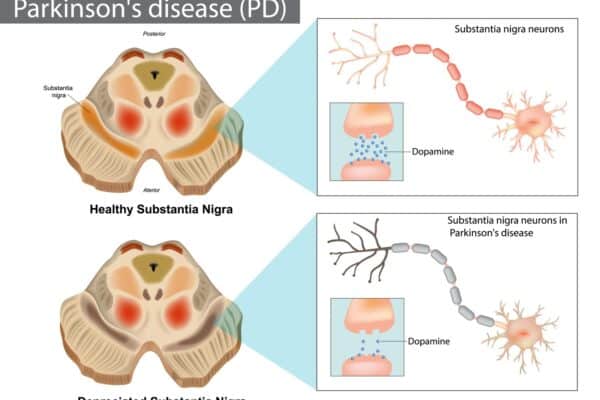
Pharmacology of Antihypertensive agents
Antihypertensive agents are medications used to lower blood pressure and treat hypertension. They are classified into several different categories, each with its own mechanism of action, uses adverse effects, contraindications, and drug interactions. Here’s a brief overview of the main categories and examples of antihypertensive agents: Diuretics Examples: Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ), Furosemide, Spironolactone Mechanism of action:…