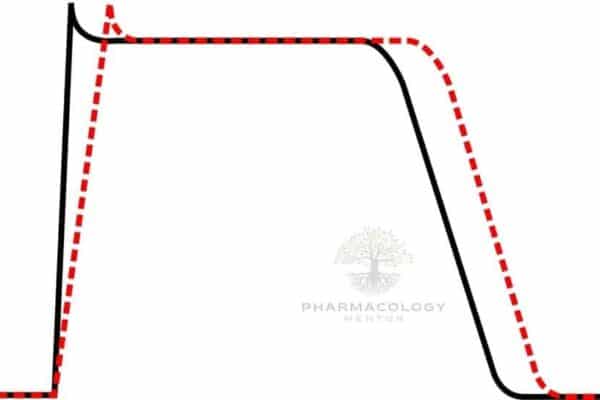
Antiarrhythmic drugs: Beta-adrenoceptor-blocking drugs (Class 2)
Introduction Beta-adrenoceptor-blocking drugs, commonly known as beta-blockers, are a class of medications with antiarrhythmic properties. These drugs work primarily through their β-receptor-blocking action and direct membrane effects. This article will talk about how Class 2 antiarrhythmic drugs work, how well they work, and how they can be used in therapy. It will mostly focus on…