Antiarrhythmic drugs: Lidocaine (Class 1B)
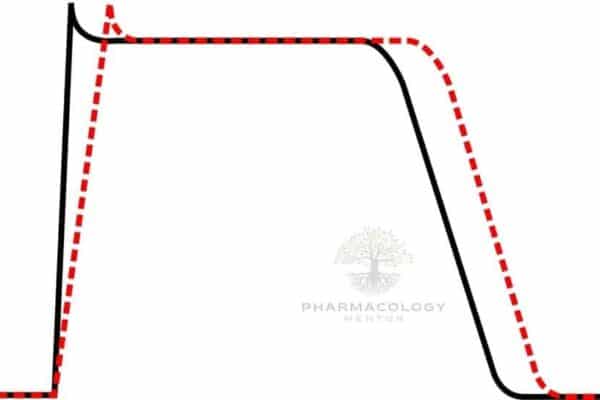
Introduction Lidocaine is a multifaceted medication primarily known as a local anesthetic, but it also has significant roles as an antiarrhythmic and analgesic agent. Classified as a Class Ib antiarrhythmic agent under the Vaughan-Williams classification, lidocaine is particularly effective in the treatment of ventricular arrhythmias. This includes its use in managing life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias that…