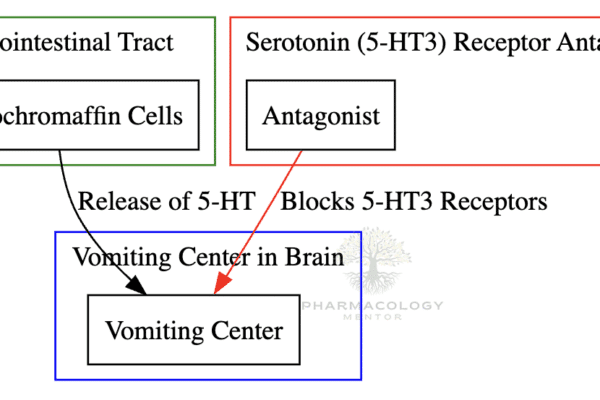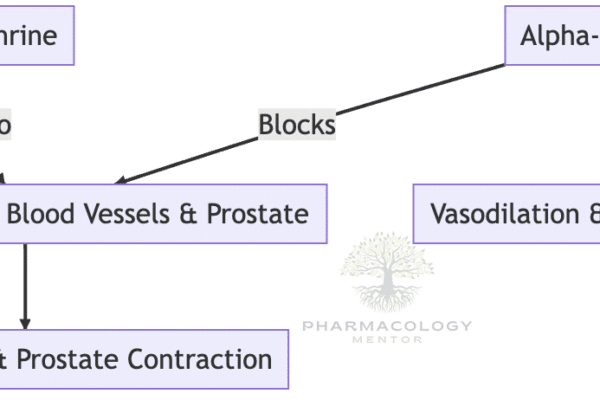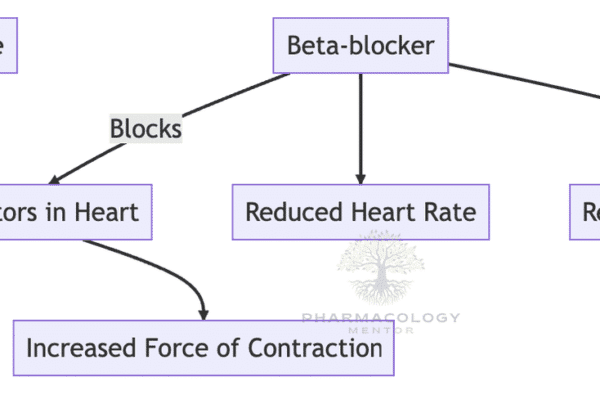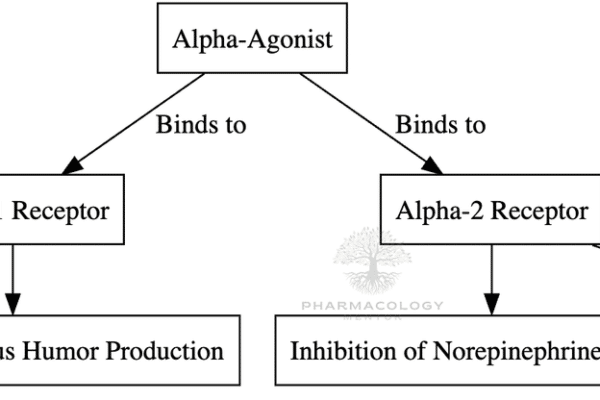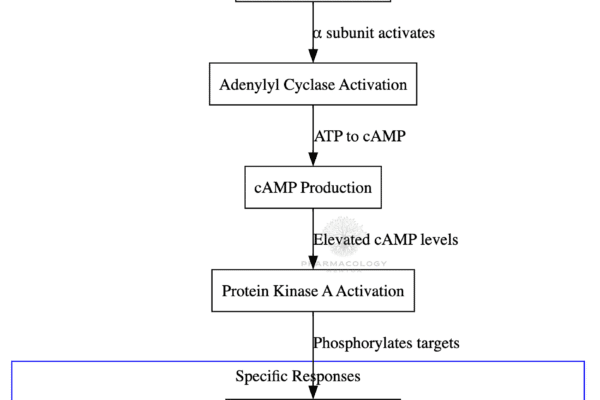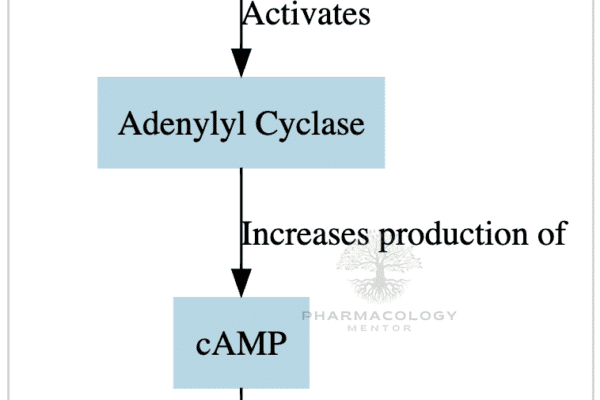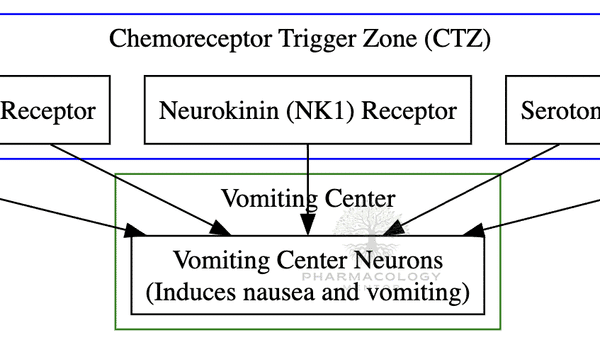
The Vomiting Center and CTZ
Vomiting is a complex reflex action that involves multiple areas of the brain and various neurotransmitter systems. Central to this process are the Vomiting Center (VC) and the Chemoreceptor Trigger Zone (CTZ). Let’s delve deeper into their roles, the receptors involved, and their significance in conditions like postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV) and chemotherapy-induced nausea…