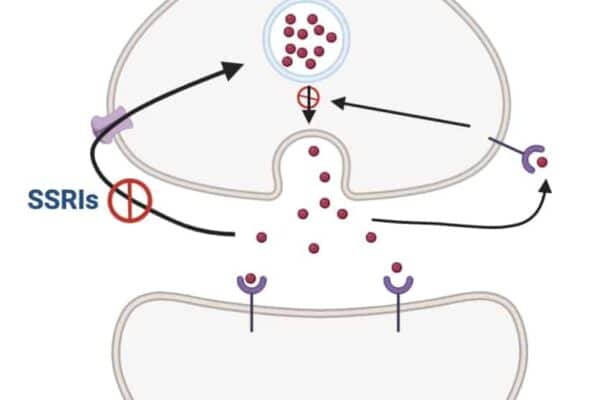
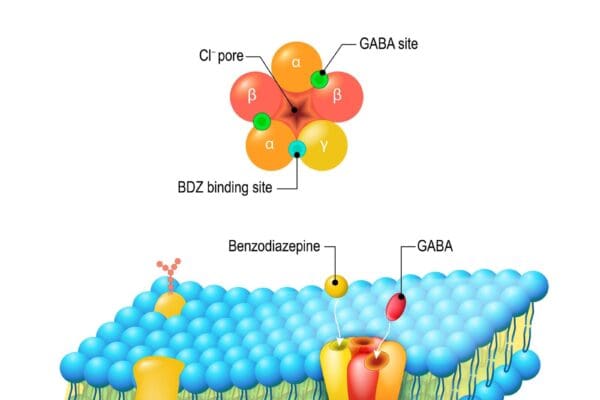
Barbiturates: Mechanisms, Types, and Clinical Relevance
Introduction: Barbiturates are a class of drugs known for their sedative-hypnotic effects, used in the management of conditions like seizure disorders, neonatal withdrawal, insomnia, preoperative anxiety, and the induction of coma for increased intracranial pressure. Additionally, they have a role in inducing anesthesia, with thiopental being a notable example introduced back in 1934 for this…