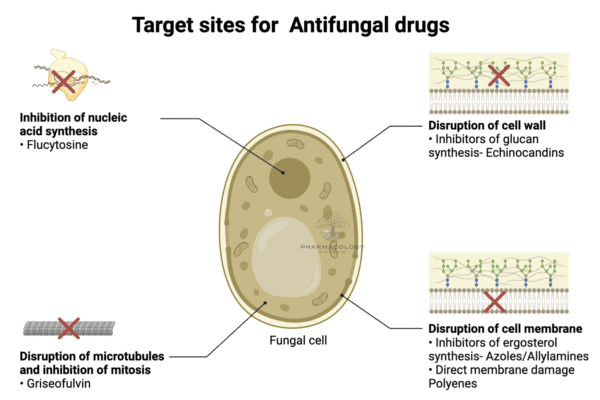
Drugs for Congestive Cardiac Failure
1. Introduction Congestive heart failure (CHF) is a condition in which the heart is unable to pump blood effectively, leading to fluid accumulation in the lungs and other body tissues. Various medications are available to manage CHF, which can help alleviate symptoms and improve the patient’s quality of life. This article will explore the classification…