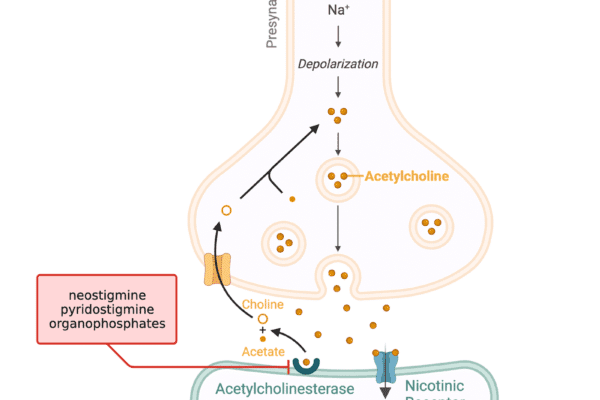
Atropine/Belladonna/Datura Poisoning: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Introduction Atropine/belladonna poisoning is a potentially dangerous and life-threatening condition caused by ingesting or coming into contact with the toxic compounds found in plants like deadly nightshade (Atropa belladonna) and other related species. This article will explore the origins of atropine and belladonna, common causes of poisoning, symptoms to look out for, diagnosis, treatment options,…