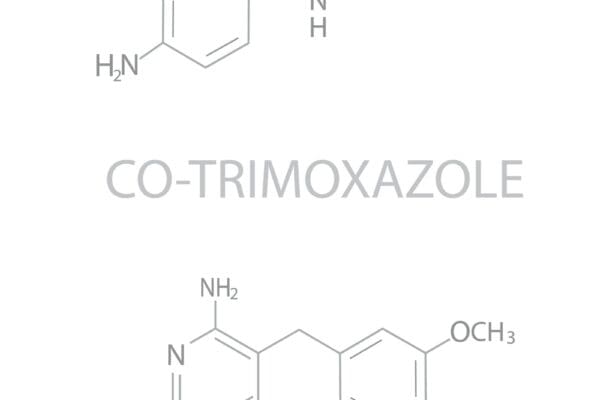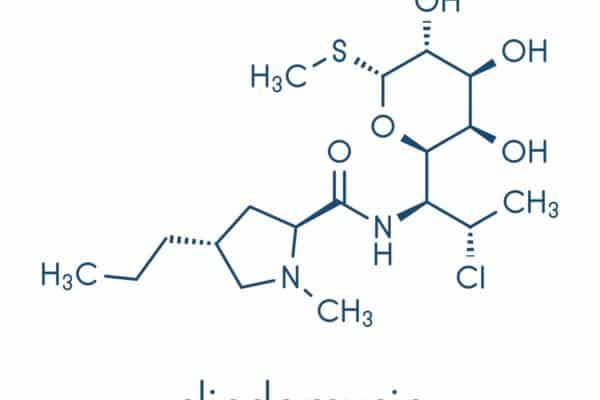
Clindamycin: a lincosamide antibiotic
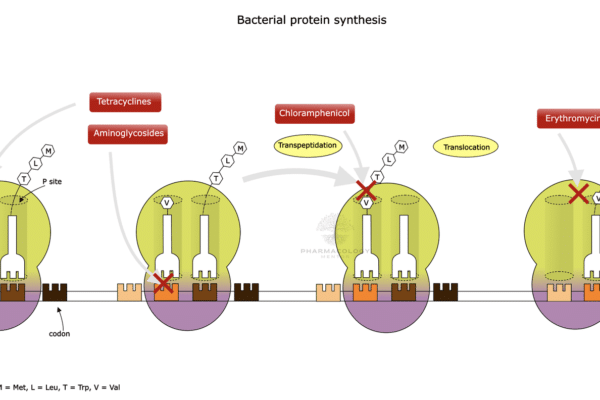
Clindamycin is a lincosamide antibiotic that is used to treat a wide variety of bacterial infections. It is particularly effective against certain types of Gram-positive bacteria and anaerobic bacteria. Below is a detailed analysis of the pharmacology of clindamycin along with recent updates regarding its usage and resistance patterns: Mechanism of Action Clindamycin operates by…