Drug Specificity: A Key Factor in Pharmacological Actions
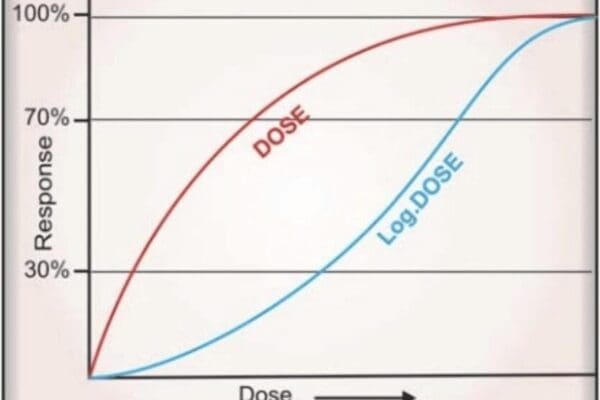
Drug specificity is an important concept in pharmacology that refers to the range of actions a drug can produce. Understanding drug specificity is crucial for healthcare professionals, researchers, and patients alike, as it helps to predict the drug’s effects and potential side effects. Here, we explore the factors that govern drug specificity and provide examples…