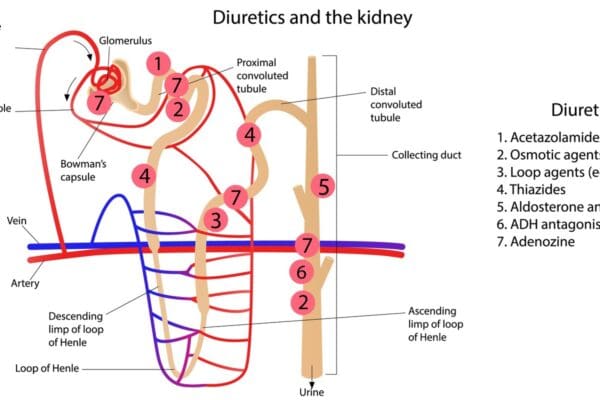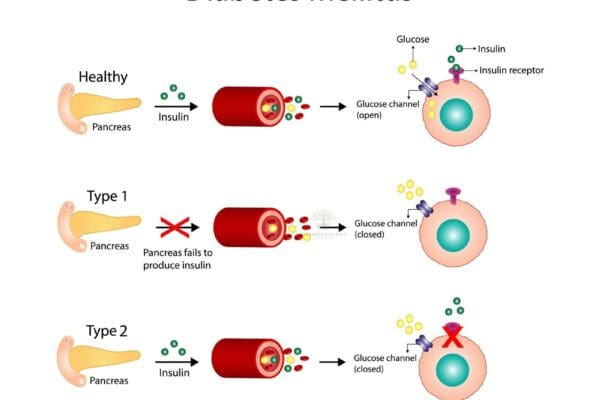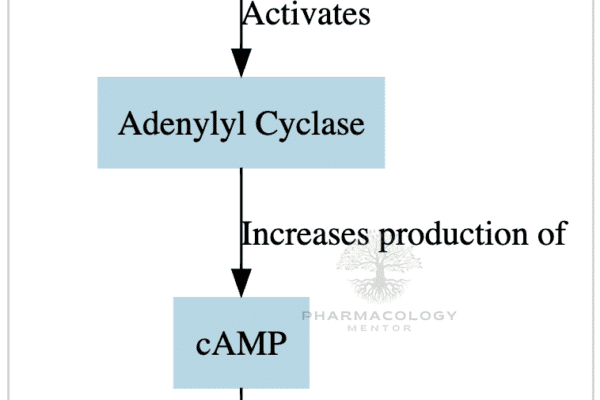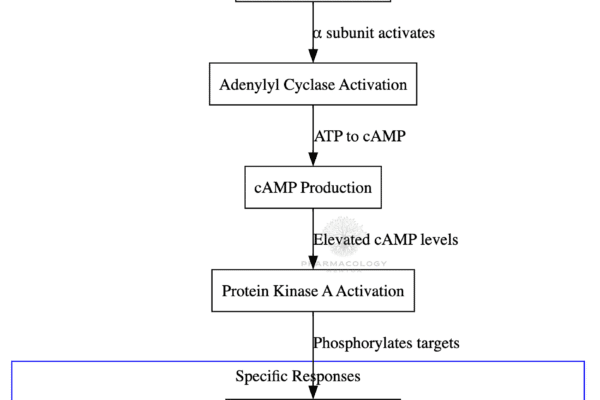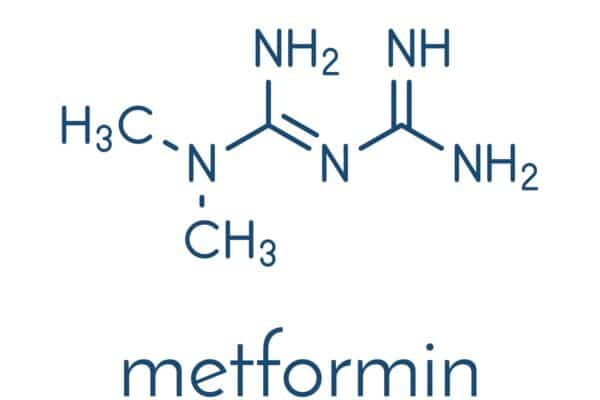
Metformin: The Most Popular Biguanide Explained
Metformin belongs to Biguanides, a class of oral antidiabetic drugs that are used to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus. The most commonly used biguanide is metformin. Mechanism of action Pharmacokinetics Biguanides are absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and distributed throughout the body. They are not metabolized in the liver and are excreted unchanged in the…