Sodium Channel Blockers (SCBs)
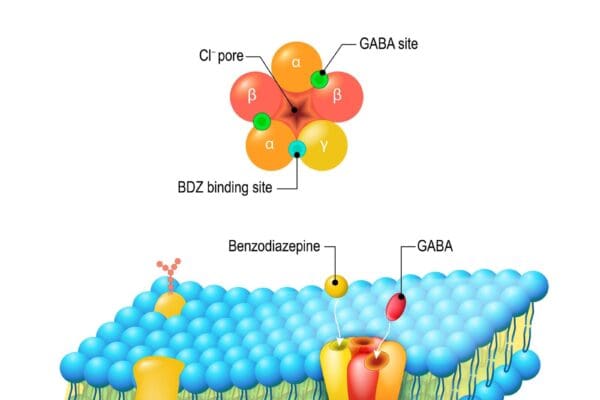
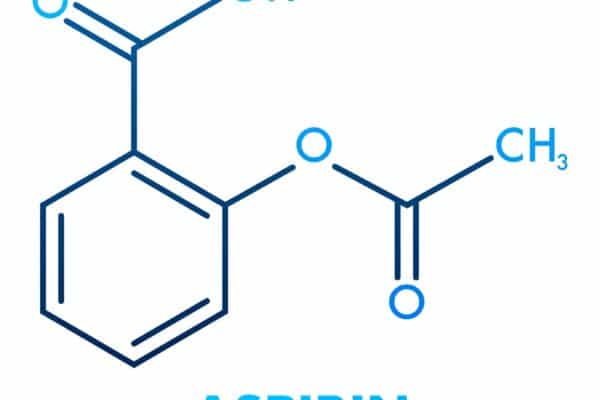
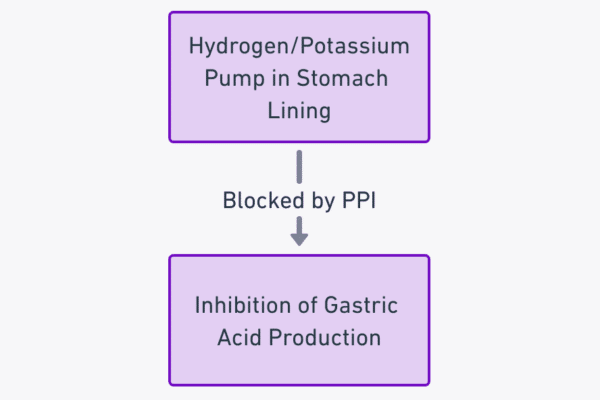
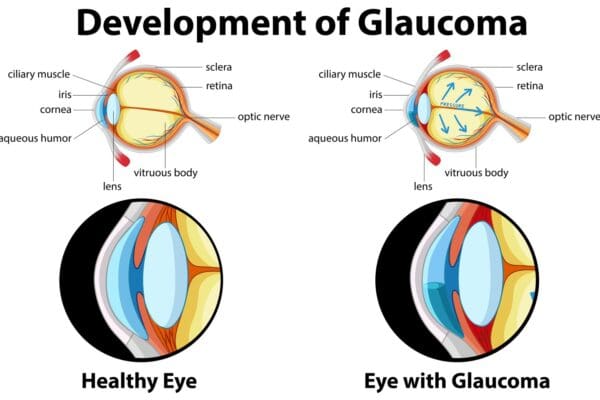
Sodium Channel Blockers Introduction Sodium Channel Blockers (SCBs) are pivotal in medical therapeutics. These drugs primarily target the sodium channels in cells, inhibiting the flow of sodium ions. This action is crucial in regulating electrical impulses, especially in the heart and nervous system. Their significance in treating various cardiac and neurological conditions is unparalleled. Classification…