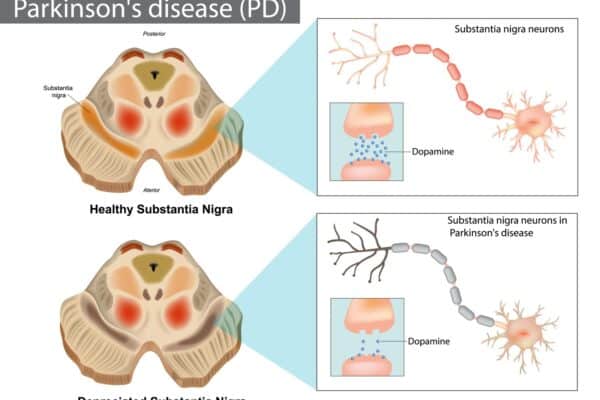
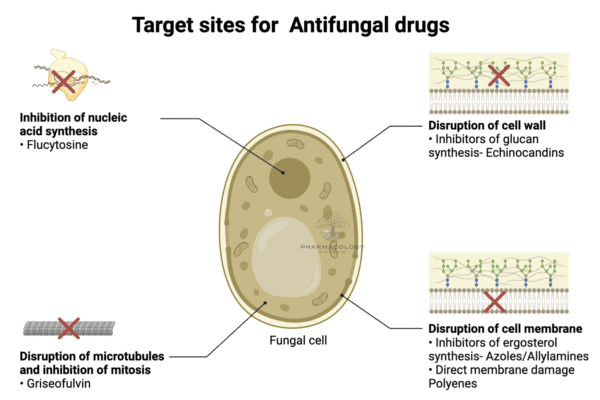
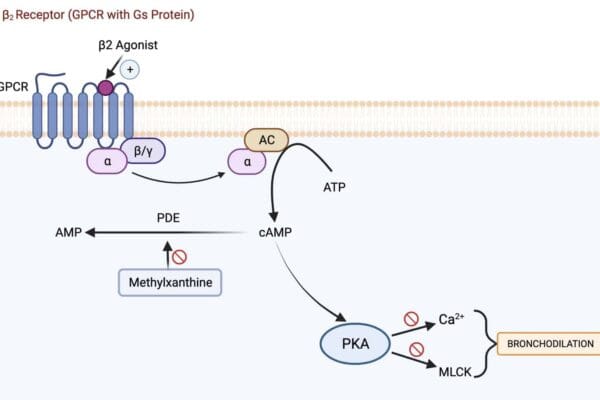
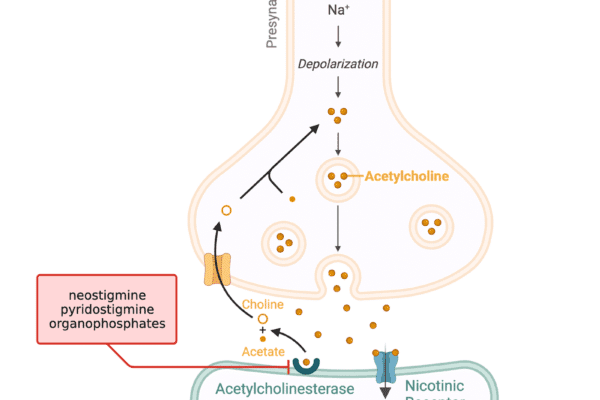
Antiepileptic Drugs
Introduction Antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) are medications used to treat epilepsy, a neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures. There are several classes of AEDs, each with different mechanisms of action, therapeutic uses, and adverse effects. In this answer, we will discuss the classification of AEDs, along with examples of drugs in each class, their mechanism of…